Introduction to Wildfire Events
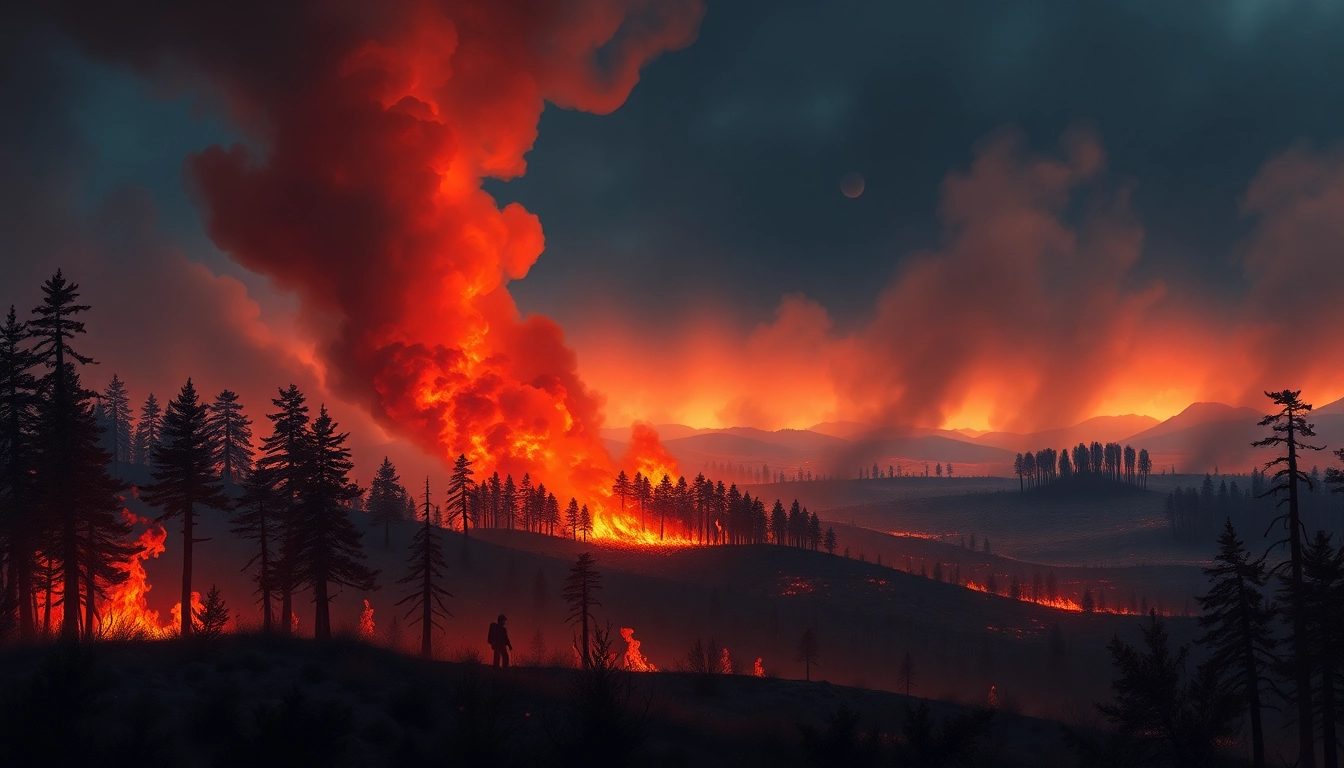
Wildfire events are significant ecological phenomena characterized by uncontrolled fires that can cause extensive destruction to both natural and human-made environments. These events can arise under specific conditions, leading to destructive outcomes that affect not just the landscape but the ecosystem, human health, and the local economy. Understanding wildfire events is crucial, particularly in areas prone to such incidents. In this comprehensive analysis, we will delve into what wildfire events are, their causes, historical insights, their impacts on the environment, and strategies for prevention and management. For more information on wildfire events, you can explore resources provided by wildfire events.
What are Wildfire Events?
Wildfire events refer to uncontrolled fires that burn in forests, grasslands, and other wildland areas. These fires can be ignited by various factors, including lightning strikes, human activities, and extreme environmental conditions like drought. Wildfires can spread rapidly, driven by wind, topography, and available fuels, presenting severe threats to life, property, and the environment.
Typically, wildfires are classified into three types: surface fires, ground fires, and crown fires. Surface fires burn along the ground and affect litter and low shrubs, while ground fires burn underground in organic matter and root systems. Crown fires, the most dangerous, spread through the tops of trees, fueled by dry foliage. A better understanding of these classifications can help in managing and preparing for potential wildfire events.
Key Factors Leading to Wildfire Events
A combination of natural and human-induced factors contributes to the occurrence of wildfire events. Understanding these factors is essential for preventive measures:
- Weather Conditions: Hot, dry, and windy conditions increase the likelihood of wildfires. Prolonged droughts and unusually high temperatures can create optimal environments for fires to ignite and spread.
- Vegetation and Fuel Loads: Areas with an abundance of dry vegetation serve as fuel for wildfires. Certain ecosystems, such as grasslands and forests with dense underbrush, are particularly vulnerable.
- Human Activities: Approximately 85% of wildfires are caused by human actions, including campfires left unattended, discarded cigarettes, and intentional arson. Activities like land clearing and agricultural burning can also escalate wildfire risks.
- Climate Change: Changes in climate patterns have led to increased temperatures and altered precipitation levels, further exacerbating the risk and frequency of wildfires. Following years of above-average temperatures, regions can experience more severe droughts that heighten these risks.
Historical Wildfire Events: Lessons Learned
Examining historical wildfire events can provide invaluable insights into prevention and response strategies. One prominent example is the 1910 Great Fire in Idaho and Montana, which burned over three million acres and destroyed several towns. This catastrophe highlighted the need for coordinated firefighting efforts and ultimately led to the establishment of policies focused on wildfire suppression.
Another significant event was the 2003 Southern California wildfires, which caused extensive property damage and loss of life. This prompted the implementation of stricter building codes and improved urban planning strategies to mitigate risks in fire-prone areas. Moreover, these events illustrated the importance of community engagement and preparedness efforts, prompting initiatives that seek to educate and distribute resources among residents.
Impacts of Wildfire Events on the Environment
The impacts of wildfire events are multidimensional, affecting ecosystems, human health, and economic stability.
Effects on Ecosystems and Biodiversity
While wildfires can have devastating effects, they also play a natural role in many ecosystems. Certain species rely on fire to regenerate. For instance, some pine trees require heat from fire to open their cones and release seeds. However, destructive wildfires can lead to habitat loss, change species composition, and create ecological imbalances. These changes can result in long-term consequences for biodiversity, particularly if the fire intensity exceeds the adaptive capacity of local flora and fauna.
In addition, soil erosion is a major concern post-wildfire, as vegetation that normally retains soil can be removed. This erosion can lead to sedimentation in waterways, negatively impacting aquatic habitats and potentially harming water quality.
Human Health Risks During Wildfire Events
Wildfire events significantly affect human health through air quality degradation, which can exacerbate respiratory issues, cardiovascular problems, and other health conditions. The smoke produced can lead to hazardous air quality levels, even miles away from the fire. Vulnerable populations, including children and the elderly, are particularly at risk.
Moreover, direct exposure to fire can result in injuries or fatalities. The psychological impact of living near wildfire-prone areas can also lead to chronic stress and anxiety for individuals and communities preparing or recovering from wildfire events.
Economic Consequences of Wildfire Events
The economic impact of wildfire events can be staggering. Direct damages include loss of property and infrastructure, as well as firefighting costs, which can escalate rapidly when addressing large-scale fires. Insurance claims can lead to increased premiums and financial hardship for affected individuals and communities.
Beyond immediate financial losses, wildfires can disrupt local economies dependent on tourism, agriculture, and natural resources. Long-term recovery can take years, particularly for industries reliant on healthy ecosystems, leading to ongoing economic instability in the affected areas.
Wildfire Prevention and Safety Strategies
Effective preventive measures and community engagement can significantly reduce the risk of wildfire events and enhance preparedness.
Building Fire-Resistant Structures
To mitigate risks in fire-prone areas, construction methods must focus on creating fire-resistant structures. This includes using non-combustible building materials, maintaining defensible space by clearing away vegetation near homes, and utilizing fire-resistant landscaping methods. Comprehensive zoning regulations can also ensure that new developments are strategically placed away from high-risk zones.
Moreover, homeowners are encouraged to invest in fire-resistant features such as ember-resistant vents, double-paned windows, and fire-retardant coatings for roofs and walls. Home assessments can help identify weaknesses in fire resistance and guide necessary improvements.
Creating Firebreaks and Controlled Burns
Firebreaks are strategically cleared areas that can halt the spread of wildfires by removing flammable vegetation. Creating and maintaining firebreaks in both urban and wildland areas is a proactive way to protect homes and manage forests. Controlled burns, another effective strategy, involve intentionally igniting fires under controlled conditions to reduce excess fuel loads and promote ecological health.
Collaboration among landowners, forestry departments, and firefighting agencies is essential to establish controlled burn programs. Education on these techniques can help communities understand their purpose and reduce resistance to their implementation.
Community Engagement in Fire Safety
Community involvement is key to wildfire preparedness. Programs can facilitate public awareness and educational campaigns about wildfire risk reduction, safe evacuation procedures, and emergency response plans. Local organizations can host events, workshops, and demonstrations to engage the community and foster collaboration among residents, fire agencies, and environmental organizations.
Communities can also participate in initiatives like Firewise USA, which empowers residents to adopt fire-safe practices. By fostering a culture of preparedness, communities can enhance resilience to wildfire events and safeguard lives and property.
Technological Advances in Managing Wildfire Events
Technological innovations play a significant role in improving wildfire management practices, including fire detection, monitoring, and response strategies.
Utilization of Drones and Satellite Technology
Drones equipped with thermal imaging cameras are becoming increasingly popular for wildfire detection and assessment. They provide real-time imagery that can help emergency services identify fire hotspots and provide critical information for response strategies. Satellite-based monitoring systems can provide broader visibility, allowing authorities to track wildfires and analyze their behavior across vast landscapes.
This technology not only enhances situational awareness but also enables better resource allocation and response planning, significantly improving firefighting efficiency and effectiveness.
Firefighting Equipment Innovations
Innovation within firefighting equipment has also grown, with the development of advanced firefighting vehicles, aerial firefighting systems, and personal protective gear. Self-contained breathing apparatus (SCBA) and heat-resistant suits allow firefighters to operate safely in hazardous conditions. Furthermore, aerial systems like water-dropping helicopters and fixed-wing aircraft are vital for rapidly combating large fires from the air, drastically reducing fire spread potential.
Predictive Modeling and Analytics
Predictive modeling tools that incorporate machine learning algorithms analyze historical fire data and environmental conditions to forecast wildfire risks. These tools can assess factors such as vegetation moisture levels, weather patterns, and local human activities. Utilizing predictive analytics can help agencies effectively allocate resources, anticipate fire behavior, and establish prevention strategies based on probable outcomes.
Upcoming Wildfire Events and Community Programs
Staying informed about upcoming wildfire events and community programs is crucial for individuals and organizations looking to enhance their preparedness.
Major Conferences and Gatherings on Wildfire Safety
Regular conferences and workshops centered around wildfire management and safety serve as key opportunities for stakeholders to collaborate, share insights, and learn about the latest innovations. Events organized by national and local organizations, such as the Association for Fire Ecology or the National Interagency Fire Center, host expert-led discussions and training sessions focused on best practices for wildfire prevention and response.
Volunteer Opportunities in Wildfire Management
Volunteering in wildfire management can provide community members with practical knowledge and valuable experiences. Organizations often seek volunteers for wildfire preparedness programs, training sessions, and community engagement activities. Participating in these programs helps individuals contribute to their community’s safety while acquiring skills that benefit future wildfire response efforts.
How to Stay Informed on Wildfire Events in Your Area
Awareness of local wildfire conditions can significantly enhance safety. Subscribing to local fire department alerts, utilizing mobile applications for real-time updates, and engaging with community safety initiatives can provide timely information. Public resources, such as state forestry agencies or the National Interagency Fire Center, offer information on current wildfire incidents and preparedness tips, helping residents stay informed and proactive.